Transition Finance Weekly - 8/7/2025
Colorado Fast-Tracks Clean Energy, “Solar for None,” Demand Response Expands
Exploring the policy, politics, and economics of the clean energy transition
Each week here in Transition Finance Weekly, researchers and analysts from Pleiades Strategy summarize the top stories and trends related to the policy, politics, and economics of the clean energy transition in the states.
WE WANT TO HEAR FROM YOU. What would you like to see in this newsletter? What kinds of developments would you like us to track? You can reach us at newsletter@pleiadesstrategy.com.
Subscribe to our Substack (it’s free!)
1. States Race the Clock on Clean Energy Tax Credits
With federal clean energy tax credits phasing out, there’s a short window to lock in progress. Some states are getting the job done.
In Colorado, Gov. Jared Polis is moving fast to secure the state’s clean energy industry. In a new directive issued last week, he called on state agencies to expedite clean energy projects to help residents and utilities dodge tariff shocks and take advantage of federal credits before they disappear. The state also launched a new online hub to help Coloradans access clean energy rebates and bill assistance.
In Minnesota, the public utility commission has asked utilities to share how they plan to maximize the federal clean energy credits before the truncated deadlines — and asked what actions the state can take to mitigate the worst negative impacts of the reconciliation bill.
Meanwhile, in Maine, the utility commission issued an RFP in July for 1,600 GWh of clean energy, with a strong preference for projects on PFAS-contaminated and brownfield sites.
Gov. Polis in Colorado: “Today we are taking action to ensure that Coloradans can easily access clean energy savings, especially ones that expire soon. We continue to do all we can to make people aware of how you can reduce costs on energy bills and keep money in your pocket. That’s what the launch of this new tool and executive action are all about.”
2. EPA Moves to Kill “Solar for All”
$7B in solar grants for low-income communities is on the chopping block.
The Trump administration is reportedly preparing to cancel the $7 billion Solar for All program, with termination letters from the EPA to the 60 grantees — including state agencies, tribes, and nonprofits — expected to be sent out this week.
The funds have already been contractually obligated to grantees (though mostly not yet disbursed), meaning that the government has entered into a binding agreement to allocate these funds in a specific way.
Solar for All was designed to deploy more than 4GW of distributed solar for low-income and disadvantaged communities, increasing total residential solar capacity for these households by a third over five years while delivering at least 20% in household savings. California ($560M) and Texas ($405M) grantees were designated to receive the largest shares of funds.
3. Whitmer Appointee to Reshape Utility Commission
Her new MPSC appointee, replacing a transparency and clean energy booster, has consumer advocates wary.
Alessandra Carreon, who fought DTE Energy on rate hikes and pushed for more industry transparency and ambitious clean energy policies, has been removed in a “highly unusual move” from the Michigan Public Service Commission. Her replacement? Shaquila Myers, a former Chief of Staff for Speaker Joe Tate — who as Speaker oversaw both Michigan’s 100% clean legislation and a sweetheart deal for datacenters last year. As Chief of Staff to Tate, Myers reportedly warned against taking actions that would “upset” DTE and Consumers Energy.
The MPSC will decide on DTE and Consumers Energy’s requests for $1 billion in rate hikes and on their Integrated Resource Plans in the next few years. DTE has been under scrutiny for thousands of low income shutoffs, skyrocketing rates, and record power outages.
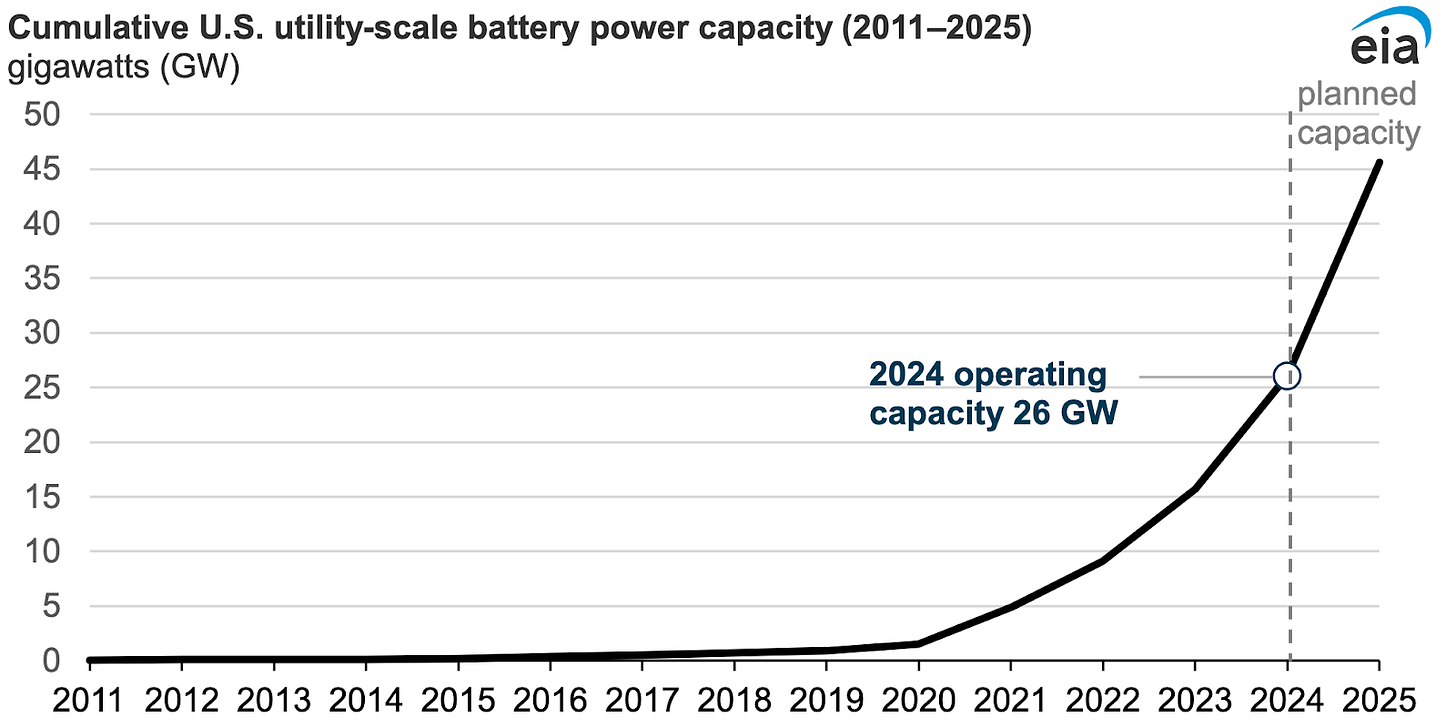
4. Batteries to the Rescue
Battery storage is increasingly a core contributor to the nation’s capacity and grid stability.
Source: Energy Information Agency (2025)
Almost a third of the new capacity Georgia Power is proposing in its energy plan is new gas generation. But there’s good news, too: they plan to build 10 new battery facilities totaling 3,022 MW, and two solar-plus-storage projects. That’s on top of 765 MW of battery capacity already under construction.
They’ve seen the light: solar and other renewables paired with battery storage are one of the fastest, cheapest, and most scalable ways to bring new capacity online, and at a time of spiking demand, speed matters. They also understand that Georgia’s capacity to accommodate more gas generation is limited by a pipeline infrastructure that’s already full.
Nationwide, battery capacity grew by two-thirds in just one year, as battery technology matures and as utilities large and small learn that having battery components in their systems gives them flexibility to maintain a more stable grid during extreme weather and other strains.
5. Google Adopts Demand Response at AI Data Centers
Google establishes precedent for how to integrate major load flexibility in long-term planning.
Google has signed new agreements with Indiana Michigan Power and the Tennessee Valley Authority to integrate demand response at its data centers, making it the first major tech firm to voluntarily scale this capability across machine learning operations and in the utility’s long-term planning.
Demand response allows utilities to scale back power delivery at peak times when the grid is struggling to deliver. This helps maintain grid stability at peak moments while also reducing the need to build capacity to handle them — and that can get data centers online faster. One outcome? Huge potential cost savings for all utility customers.
The initiative builds on prior pilots, including a successful 2023 project with Omaha Public Power District, where Google curtailed machine learning-related power use during three grid stress events.
Google’s Michael Terrell: “Research shows that even a small amount of flexibility for large energy loads, like [machine learning], during peak times can reduce the need to build new power plants while accommodating new energy loads much faster.”
SPOTLIGHT: Flood Recovery Takes a Backseat to Mid-Decade Redistricting
Texas' record-breaking floods killed more than 130 people, but instead of tackling climate resilience, the GOP hijacked the state legislature’s special session to push a redistricting plan and “anti-ESG” legislation. This has driven Democratic legislators out of the state to deny the GOP a quorum, and brought proceedings to a halt.
Meanwhile: no flood recovery bills have passed and thousands of Texas families are left to fend for themselves after their homes have been damaged or destroyed.







I’m seeing money moving from solar this week to BESS and datacenters. Still respect stance on natural gas powered datacenters. But the BESS ITC is softening the blow as solars time runs out.